Instructions
Complete all problems showing your work. Use proper significant figures throughout.
Important: Review the Study Guide for formulas and conversions you'll need to memorize!
Section A Measurement & Significant Figures
📚 Review: Significant Figures LessonProblem 1
Record the volume of water in the graduated cylinder to the correct number of significant figures.
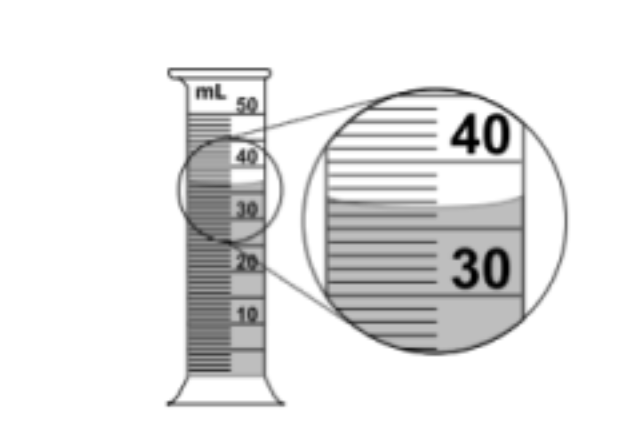
Problem 2
How many significant figures in the following values?
- a. 35.0 cm
- b. 0.089 mL
- c. 273.00°C
- d. \(1.0890 \times 10^{-6}\) nm
Problem 3
Round the answers to the following to the correct number of significant figures:
- a. \(35.00 \times 1.4 =\)
- b. \(23.506 \div 21.00 =\)
- c. \(23.016 + 10. =\)
- d. \(109.00 - 57.9145 =\)
Section B Conceptual Understanding
Problem 4
What is the difference between mass and volume?
Section C Density Calculations
Problem 5
A block of wood weighing 15.0 g measures 2.4 cm on each side. What is its density? Will it sink or float in water (Density of water = 1.0 g/cm³)?
Problem 6
A chunk of metal weighing 56.0 g is dropped into 100.0 mL of water, causing the water level to rise to 124.0 mL. Calculate the density of the metal.
Problem 7
Gold has a density of 19.3 g/cm³. What would the mass of 2.5 L of gold be?
Section D Unit Conversions
📚 Review: Unit Conversions LessonProblem 8
Convert the following:
- a. 78.2 miles = _______________ km
- b. 2500 km = _______________ inches
- c. 2.1 gallons = _______________ Liters
- d. 20.0 kcal = _______________ Joules
Section E Classification of Matter
Problem 9
Identify each of the following as a physical or chemical change:
- a. Dry ice sublimes into a vapor.
- b. A shirt is burned when a hot iron is placed on it for too long.
- c. Silver tarnishes as it reacts with nitrogen in the atmosphere.
- d. Alcohol evaporates quickly.
- e. A glass bottle shatters when it falls.
Problem 10
Label the following as elements, compounds, homogeneous mixtures, or heterogeneous mixtures:
- a. carbon
- b. milk
- c. iron filings mixed with sand
- d. mint chocolate chip ice cream
- e. potassium permanganate
Section F Thermochemistry & Calorimetry
Problem 11
Fill in the blanks:
- a. A ____________ is used to measure the kinetic energy of the particles of a substance.
- b. A ____________ is used to study the heat transfer between two substances.
Problem 12
Water has a specific heat of 4.18 J/g°C. Aluminum has a specific heat of 0.89 J/g°C. Two 50.0 g samples of water and aluminum absorb equal amounts of heat. Which substance will show the greater temperature difference?
Problem 13
When two objects at different temperatures are placed in direct contact, the heat lost by the warmer object will be ____________ the heat gained by the colder object.
Problem 14
In an exothermic reaction, heat is ____________ the surroundings.
Problem 15
Complete the following energy unit conversions:
- a. 25,000 cal = __________ J
- b. 120 Cal = __________ J
Problem 16
Complete the following temperature conversions (K = °C + 273):
- a. 100°C = ____________ K
- b. -55°C = ____________ K
- c. 450 K = ____________ °C
Problem 17
A hot piece of metal is dropped into cold water.
- a. How will their temperatures compare after a significant amount of time passes?
- b. Which substance is losing heat and which is gaining heat?
- c. How does the heat lost by one substance compare to the heat gained by the other substance?
Problem 18
Complete the following calculations using \(q = mc\Delta T\):
a. A 56.0 g sample of Aluminum (\(C_{Al} = 0.89\) J/g°C) has an initial temperature of 34°C. What will its final temperature be after it absorbs 35,000 J of energy?
b. How much heat is required to change the temperature of 11.5 g of copper (\(C = 0.385\) J/g°C) by 15.0°C?
c. 100.0 g of water (\(C = 4.18\) J/g°C) undergoes a temperature change from -15.0°C to 25.0°C. Calculate the heat energy absorbed by the water.
d. A 55.0 g piece of metal is heated to 99.8°C and dropped into a calorimeter containing 225 g of water at 21.0°C. The final temperature of the water is 23.1°C. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. (\(C_{water} = 4.18\) J/g°C)
Problem 19
75.0 mL of water is used for a calorimetry experiment.
- a. Explain how you would determine the mass of water that was used.
- b. Calculate the mass of 75.0 mL of water.
Problem 20
Before starting a calorimetry experiment, a sample of metal was placed in a beaker of boiling water. The metal was allowed to remain in the boiling water for 10 minutes, then its initial temperature was recorded as 100°C. How was the initial temperature of the metal determined without directly measuring its temperature?
Problem 21
The data from a calorimetry experiment in which a piece of metal was heated, then added to a sample of water in a calorimeter is presented below:
| Measurement | Trial One |
|---|---|
| Mass of Metal | 65.0 g |
| Volume of Water in Calorimeter | 100.0 mL |
| Initial Temperature of Water in Calorimeter | 21.5°C |
| Initial Temperature of Metal | 100°C |
| Final Temperature of Water in Calorimeter | 26.8°C |
- a. Calculate the specific heat of the metal. Include units.
- b. The actual specific heat for this metal is 0.320 J/g°C. What is the percent error for this experiment?
Problem 22
What is the definition of energy?